Generalisierung

Bei der Generalisierung/Spezialisierung spricht man davon, dass die Unterklasse Attribute und Methoden der Oberklasse erbt. Die Unterklasse ist eine spezialisierte Variante der Oberklasse.
PHP
<?php
class SuperClass
{
private $myPrivateAttribute;
protected $myProtectedAttribute;
protected function setMyPrivateAttribute($parameter)
{
$this->myPrivateAttribute = $parameter;
}
}
class SubClass extends SuperClass
{
// SubClass hat nun die Attribute und Methoden von SuperClass geerbt
// Der direkte Zugriff ist aber nur auf protected/public Attribute möglich
$this->myProtectedAttribute = 5;
$this->setMyPrivateAttribute($myParameter);
}JAVA
public class SuperClass {
private int myPrivateAttribute;
protected int myProtectedAttribute;
protected void setMyPrivateAttribute(int parameter) {
this.myPrivateAttribute = parameter;
}
}
public class SubClass extends SuperClass {
// SubClass hat nun die Attribute und Methoden von SuperClass geerbt
// Der direkte Zugriff ist aber nur auf protected/public Attribute möglich
this.myProtectedAttribute = 5;
this.setMyPrivateAttribute(5);
}Schnittstellen
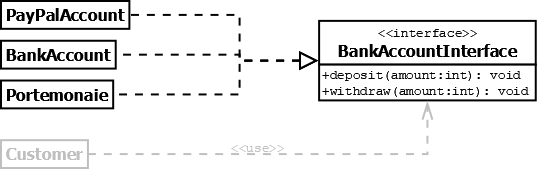
Schnittstellen bzw. Interfaces werden zur losen Kopplung zwischen Klassen genutzt. Ändert sich die Klasse, die eine Schnittstelle implementiert, kann ein anderes Objekt, dass diese Schnittstelle nutzt, unverändert bleiben. Denn die Schnittstelle selbst bleibt dieselbe. Jede Klasse, die ein Interface implementiert, muss zwanghaft alle Interface-Methoden implementieren.
Falls die Darstellung des Interfaces nicht so wichtig ist, kann auch die Lollipop- / Ball-and-Socket-Notation verwendet werden:
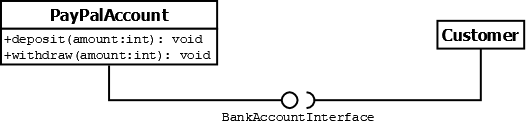
Interfaces können statische Attribute und default-Implementierungen, also nur Methodenköpfe, enthalten.
PHP
<?php
interface BankAccountInterface
{
public function deposit(int $amount): bool;
public function withdraw(int $amount): bool;
}
class PayPalAccount implements BankAccountInterface
{
private int $money = 0;
public function deposit(int $amount): bool
{
$this->money += $amount;
echo sprintf("Es wurden %s per PayPal eingezahlt.",$amount). PHP_EOL;
return true;
}
public function withdraw(int $amount): bool
{
if($this->money - $amount >= 0) {
$this->money -= $amount;
echo sprintf("Es wurden %s per PayPal gezahlt.",$amount). PHP_EOL;
return true;
} else {
echo "Der Verfügungsrahmen reicht nicht aus." . PHP_EOL;
return false;
}
}
}
class Customer
{
private array $myProducts = [];
public function payFor(StoreProduct $product, BankAccountInterface $bankAccount) : void
{
if($bankAccount->withdraw($product->getPrice())) {
echo sprintf("%s wurde gekauft.",$product->getLabel()). PHP_EOL;
$this->myProducts[] = $product;
}
}
}
function clientCode() {
$microwaveProduct = new StoreProduct('Mikrowelle',20);
$customer = new Customer();
$paypal = new PayPalAccount();
$paypal->deposit(50);
$customer->payFor($microwaveProduct,$paypal);
}JAVA
public interface BankAccountInterface {
public boolean deposit(int amount);
public boolean withdraw(int amount);
}
public class PayPalAccount implements BankAccountInterface {
private int money = 0;
public boolean deposit(int amount) {
this.money += amount;
System.out.printf("Es wurden %s per PayPal eingezahlt.%n",amount);
return true;
}
public boolean withdraw(int amount) {
if(this.money - amount >= 0) {
this.money -= amount;
System.out.printf("Es wurden %s per PayPal gezahlt.%n",amount);
return true;
} else {
System.out.println("Der Verfügungsrahmen reicht nicht aus.");
return false;
}
}
}
public class Customer {
private ArrayList<StoreProduct> myProducts = new ArrayList<>();
public void payFor(StoreProduct product, BankAccountInterface bankAccount) {
if(bankAccount.withdraw(product.getPrice())) {
System.out.printf("%s wurde gekauft.%n",product.getLabel());
this.myProducts.add(product);
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StoreProduct microwaveProduct = new StoreProduct("Mikrowelle",20);
Customer customer = new Customer();
PayPalAccount paypal = new PayPalAccount();
paypal.deposit(50);
customer.payFor(microwaveProduct,paypal);
}
}

